');
(window.slotbydup=window.slotbydup || []).push({
id: '8096091',
container: s,
size: '580,90',
display: 'inlay-fix'
});
})();
1. 一般式
y</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>a</mi><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>+</mo><mi>b</mi><mi>x</mi><mo>+</mo><mi>c</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>a</mi><mo>≠</mo><mn>0</mn><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0">
当 <mi>b</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><mn>4</mn><mi>a</mi><mi>c</mi><mo>></mo><mn>0</mn></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> 时,它与x轴有两个不同交点: (</mo><msub><mi>x</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>,</mo><mn>0</mn><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> 和 (</mo><msub><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>,</mo><mn>0</mn><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> ,其中 <mi>x</mi><mn>1</mn></msub></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> , <mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msub></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> 是方程 a</mi><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>+</mo><mi>b</mi><mi>x</mi><mo>+</mo><mi>c</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> 的两个根。

当 <mi>b</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><mn>4</mn><mi>a</mi><mi>c</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> 时,它与x轴只有一个交点: (</mo><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mi>b</mi><mrow><mn>2</mn><mi>a</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>,</mo><mn>0</mn><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0">
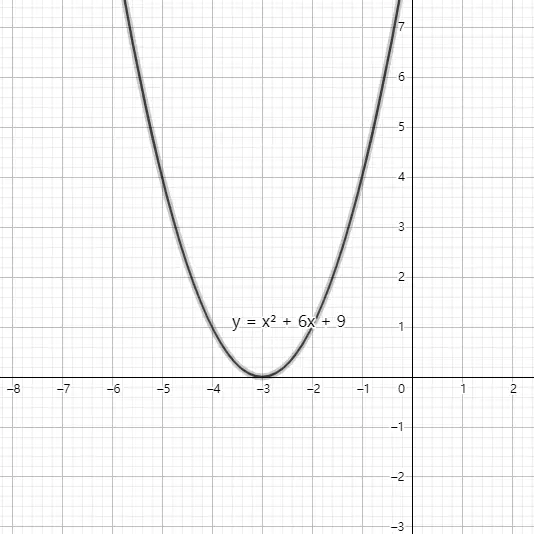
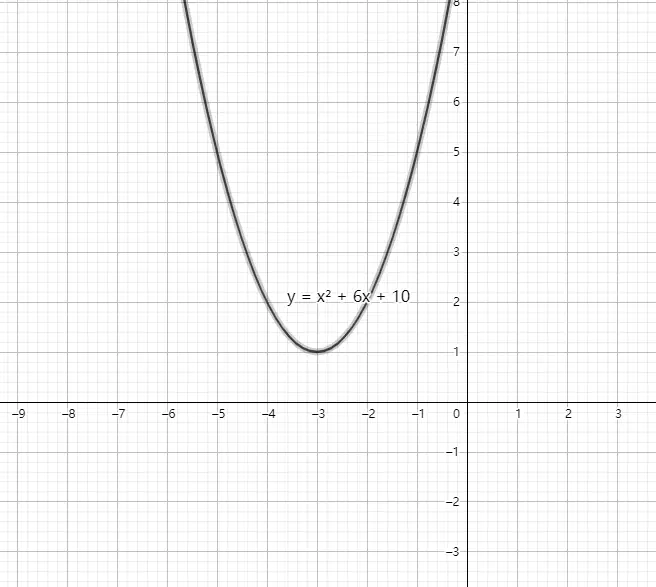
当 <mi>b</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><mn>4</mn><mi>a</mi><mi>c</mi><mo><</mo><mn>0</mn></math>" role="presentation" tabindex="0"> 时,它与x轴没有交点。
(责任编辑:admin) |